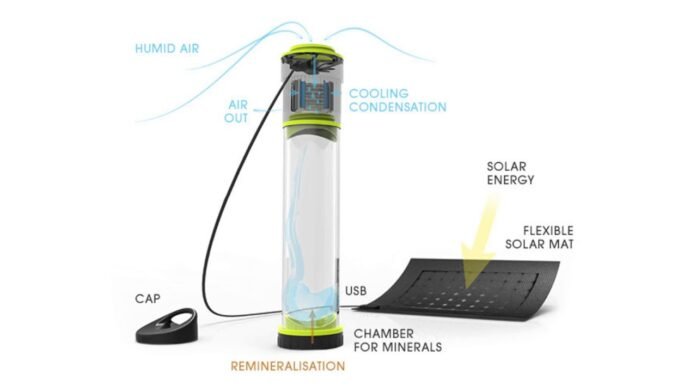
In a significant advance for environmental science, researchers from top-tier institutions such as MIT, the University of Tennessee, and Georgia Tech have created a device that can pull drinking water straight from the air using a novel fin-like system.
Water Scientific Breakthrough
The technology they developed—atmospheric Water Harvesting (AWH) based on absorption principles—represents a “game changer” in addressing the global water crisis. The system is designed to capture water vapor from the atmosphere efficiently by condensing it. This could be used as a basis for solving problems with water shortage worldwide. In other words, clean, sustainable reserves can be formed by this device using adsorption methods.
Joint Water Research Project
Scientists worked together on designing this product, conducting many experiments until they found out how it should work best. Different knowledge areas, such as materials science, environmental engineering, and atmospheric chemistry, were combined to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Impact on Environment (Water)
This breakthrough could not have come at a better time, considering that almost two-thirds (2/3) of people worldwide are predicted to live in water-stressed areas by 2030. Consequently, innovative approaches are needed to supplement traditional sources while ensuring continuous access to safe drinking supplies necessary for human life, agricultural activities, economic growth, etc.
Device Description
The machine operates through fins, which increase the surface area available for absorption, thus making more moisture collectible from the surrounding air mass. The condensed liquid is then purified to meet drinking standards, i.e., it’s safe enough. Small-size designs plus cheap parts mean that different models can be made depending on environmental conditions, ranging from dry regions to humid ones.
Comparison against Other Methods
Compared with conventional atmospheric water harvesting techniques based solely on condensation. Which are low-efficient and may fail when applied in highly arid environments, adopting a new method. This is performance-enhanced because the maximum output achievable has been considered together with the minimum use possible, improving reliability.

Prospects for the Future and Applications
Scientists predict this invention will be used widely, especially in areas where. The scarcity of clean water is frequently experienced. Thus, it will help increase local supply and make people more resilient to droughts and other climatic changes. This implies that governments, NGOs, and private companies should work together. Many devices are produced and distributed worldwide because demand keeps growing daily, mainly caused by the lack thereof.